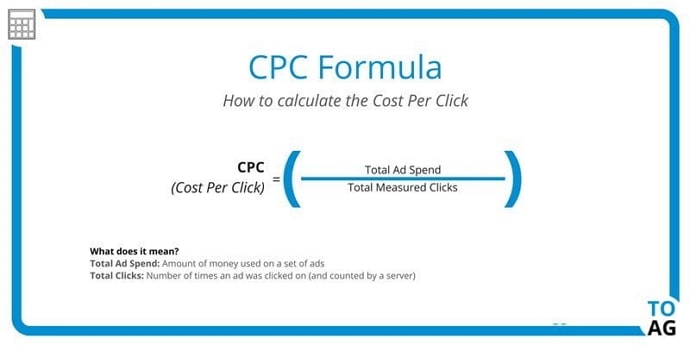
CPC (Cost Per Click) is a payment mechanism that calculates the cost per click on an advertisement or banner . It is actively used in the PPC (pay per click) model, where advertisers pay for users to click on ads and go to the target site. Ad clickers are of far greater interest and value to marketers than clickers who just viewed the ad. There are many similar arrangements, the differences of which you can learn about in a useful article https://blog.partners1xbet.com/difference-cpc-and-cpm/
In simple terms, CPC is cost per click.
Thanks to this model, you can evaluate the effect of contextual advertising by such parameters as:
- payback of banners;
- maximum cost per click;
- choosing the most effective banner format: text, video or photo banner;
- placement of advertising blocks in search results ;
- site conversion rate;
- the volume and quality of ad content.
How CPC advertising works
We must choose an advertising system – for example, Google Ads , which has all the necessary functionality. After the creation and moderation of the advertising campaign, it is put into operation.
In the search results or on one of the partner sites, the user sees an ad or banner. If they arouse interest, he clicks on them to buy / download / subscribe to the newsletter or take another targeted action on the pages where he lands.
The advertising system, followed by the web analytics system, captures the click, and as a result, the advertiser is charged at the rate at the time of the click.
Keep in mind that there are two pay-per-click schemes:
- fixed payment. Here, the advertiser himself sets the price per click and pays the agreed amount;
- auction. Used by Google advertising system. The advertiser sets the maximum cost per click, and the system then conducts an auction, giving priority to those who assign a higher Cost Per Click value. Based on the results, the final cost per click is formed.
Advantages and disadvantages of pay per click
Let’s start with the benefits:
- With a probability of 99% (one percent let’s leave it to evil competitors), only interested users click on the ad or sitelinks in it.
- Spending the budget on advertising evenly compared to paying for impressions.
- By clicks, you can collect data on segments of the target audience , because you will have data on unrolled ads in your hands.
There are also disadvantages:
- The transition of the user to the landing page does not mean that he will perform the target action there. Here it’s all about how the page is designed in terms of content , design, navigation, whether there is a CTA button or a lead form, and many other factors that affect user behavior.
- The cost of clicks can be much higher than the cost of impressions.
- The disadvantage arising from the previous one: a wide range of prices for CPC, when it will be profitable to use it in one niche, while in another it will be a banal waste of the budget. We will talk about this below.
CPC, CPM, and CPA: Differences in Advertising Payment Models
CPC is the payment for a click on an advertisement or banner during the entire time the advertising campaign is being rolled out.
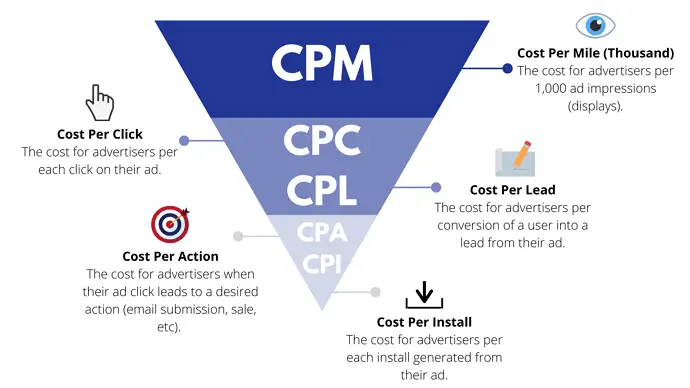
CPA (Cost Per Action) is a payment for performing a targeted action, which may include placing a product in a shopping cart, downloading a file, entering data and sending a feedback form, applying for a call, etc. This scheme can be found in the advertising tools of social networks. networks, contextual advertising systems and partner networks.
CPM (Cost Per Mile) is the cost per thousand views. Such advertising works not only for sales, but for the formation of a positive image of goods and services in particular and the company as a whole. Differs in the greatest cheapness among other payment mechanisms. It is actively used by the online media, bloggers and social networks (the same Facebook, for example).
Where pay-per-click advertising is used
There are three answers to this question.
SERP Ads
The basic and most profitable type of contextual advertising, where the user receives blocks of commercial issuance along with organic. Ads can be placed either at the top (premium impressions), or in the middle and at the bottom of the issue (the so-called remaining impressions). Advertising systems receive payment based on clicks on ads.
CCM Google
In an ideal working situation, networks’ ads appear on sites that are most relevant to users’ search queries and behavioral characteristics. For example, they will see banners about cars for sale on those sites that deal with auto parts and fuels and lubricants.
At the same time, it should be borne in mind that in ad networks, the click-through rate of an ad will be lower than that of ads on search. This is where CPM is often preferred – it’s better for users to develop an eye for banners than to hope they end up getting interested and clicking on them. This is a question of how well you need to work on the appearance of promotional materials!
Remarketing
Here you can find objective similarities with the mechanics of the Google Display Network, but there is also a significant difference. The fact is that through remarketing, the advertiser attracts (or, to be more precise, returns and even retains) those people who have previously shown interest in his product: they simply followed the links or have already made purchases. The previously described CPM and CPA are also used here.
Aspects of setting up CPC advertising
There are several rules that will allow you not to make a lot of mistakes and run HR with the greatest impact:
- Show yourself as a true marketer – research your target audience, competitors and indicate what you are going to launch advertising for: show yourself at your best, sell a product, get loyal readers, etc.
- Work with the numbers and determine the maximum allowable cost per click and the result that you want to see on it. Thus, you will insure yourself and immediately understand that the ad “didn’t work”. As a result, you quickly restructure the strategy and already work further with what works off its value.
- Do all settings strictly MANUALLY . Yes, both advertising systems have automated strategies in their toolkit – convenient for beginners, but not very good for those who fight for every ruble. Auto-settings often ignore user locations, competition levels, and product specifics. Well, the system does not know what is the use of your euro-windows from the Smolensk thousand-year-old oak, which has lain at the bottom of a forest lake! Show everything important on your own and do not trust such things to a purely system.
- Never forget remarketing . An old client is truly better than two new ones. He will be more willing to respond to your advertising activities if the last time he was satisfied with everything in terms of quality, prices and assortment. It will also take you less time to tweak the settings of the remarketing campaign, because you most likely have already studied the target audience.
- Use UTM tags to receive data about advertisements through the web analytics system. You might be surprised that an ad that you didn’t bid on heavily performed the best in terms of acceptable CPC.
Pay Per Click Advertising Optimization
First, let’s look at what affects the cost per click.
The frequency of search queries you want to implement in your ads. More frequency – higher target audience coverage and more competition. CPC will go up.
CTR of advertisements . The more users click on an ad, the cheaper the click ends up being. Content plays a very important role here: the ad must be properly designed, the text is written correctly (yes, everyone hates mistakes!), A clear and understandable call to action is formed.
Niche and business features. If you are selling snow in the winter… I mean air conditioners in the summer, then the cost per click will be incomparably higher than those who advertise plasma ovens.
Summary. How to get the most out of CPC
- Set priorities and decide on the goals and objectives of the advertising campaign. Study your audience, competitors and product. Set a CPC level that you consider excellent, acceptable, and undesirable. Decide which metrics you will monitor in web analytics systems to judge ad performance based on objective data, not personal preference.
- Set up campaigns manually. Don’t be fooled by auto-strategies, because often this is just a way to test one or another hypothesis, and you need to spend money wisely.
- Keep all settings consistent and keep track of ad impressions. See with Google Analytics , and your own CRM and sales reports.

 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  TRON
TRON  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Lido Staked Ether
Lido Staked Ether